Coretech Innovations
Coretech Innovations






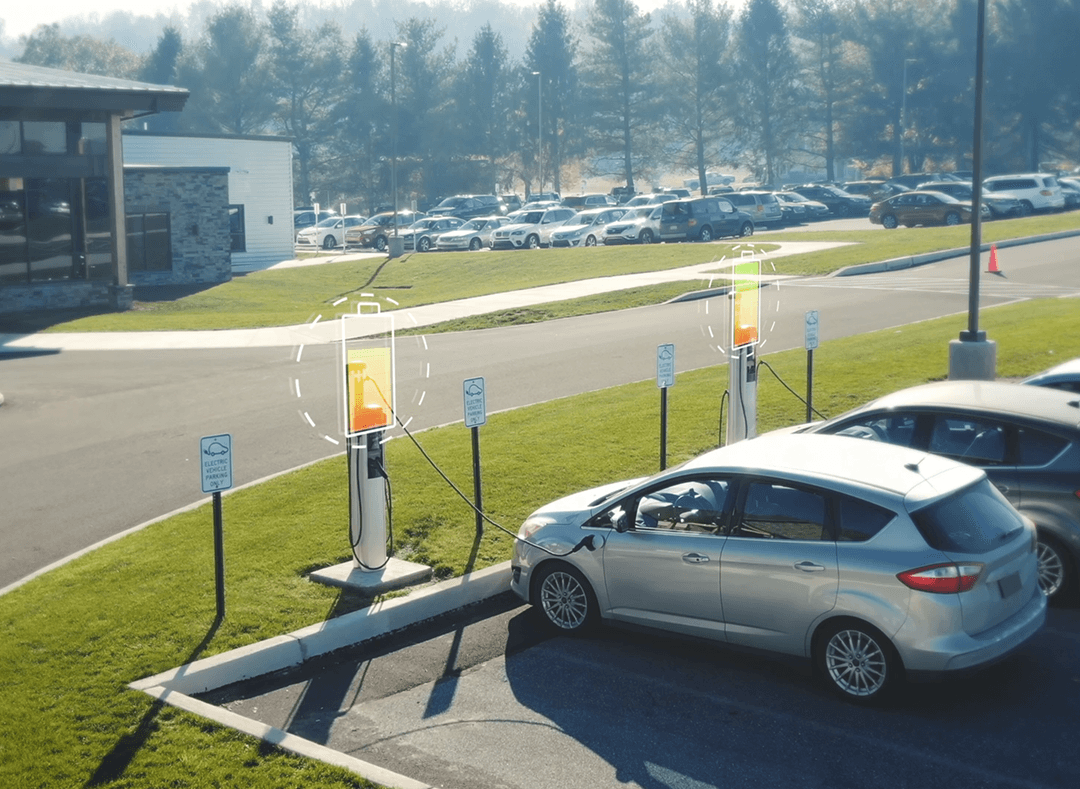
Coretech Innovations' E-Mobility Lab develops AI, IoT, Embedded Systems, R&D,Robotics, EV simulators, and Wallbox chargers for EV cars.

At Coretech Innovations, we specialize in embedded software development tailored to meet the unique needs of your projects. Our expert team combines extensive experience in both software and hardware to deliver high-performance solutions for a wide range of tech industry, including automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial automation.
At Coretech Innovations, we specialize in developing high-quality web and mobile applications tailored to meet your unique business needs. Our team of experienced developers focuses on creating intuitive, user-friendly interfaces and robust backend systems, ensuring seamless performance across various platforms. We prioritize best practices in design, coding, and testing, utilizing the latest technologies and frameworks to deliver secure, scalable, and responsive applications. Whether you need a feature-rich web app or a dynamic mobile experience, our commitment to excellence ensures that your digital solutions are both innovative and reliable, providing a superior user experience.
At Coretech Innovations, we offer comprehensive software system testing services aligned with ISTQB standards and functional safety standards, such as ISO 26262. Our testing processes ensure high-quality, reliable, and safe software systems. We leverage automation tools and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, including Jenkins, to streamline testing and deployment. This approach enables us to provide rapid feedback, efficient bug detection, and consistent quality assurance, ensuring your software meets the highest industry and regulatory standards while accelerating time-to-market.
Coretech Innovations offers comprehensive software maintenance services designed to keep your systems running smoothly and efficiently. Our services include regular updates, bug fixes, performance optimization, and security enhancements, ensuring that your software remains robust and secure. We also provide technical support and troubleshooting, helping to minimize downtime and address issues promptly. By partnering with us, you can extend the lifespan of your software, reduce operational risks, and focus on your core business activities while we handle the technical complexities.
Accelerate your EEBUS device development process and streamline your workflow with EEBUS-Hub, the cutting-edge framework designed to seamlessly integrate your devices over an EEBUS network. Whether you’re working with Software in the Loop (SiL) or Hardware in the Loop (HiL) scenarios, EEBUS-Hub provides robust support to ensure flawless performance and compatibility. Read More
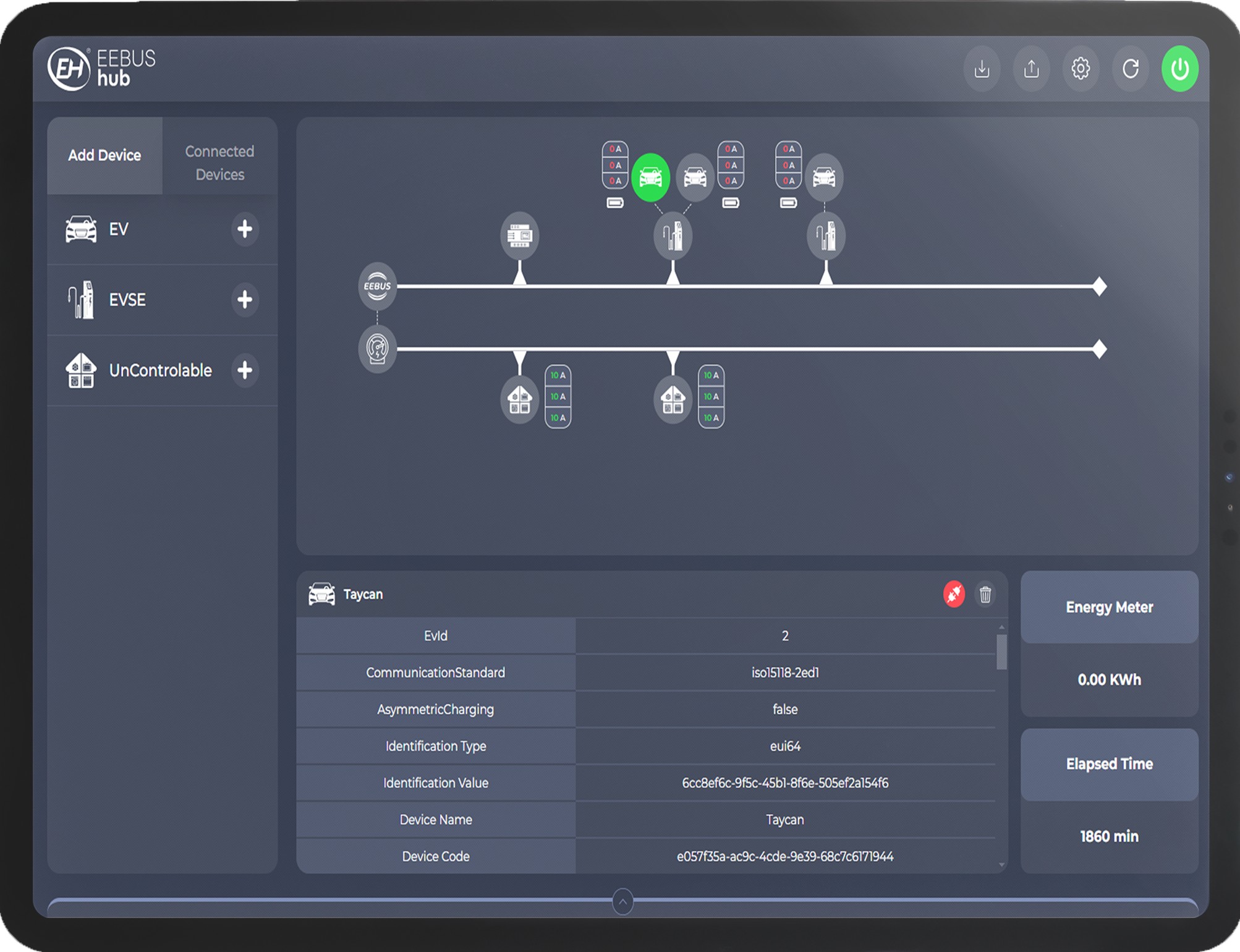







Learn how our innovative solutions are solving real-world challenges in the EV software industry. Your journey to understanding starts here !